Dr Amit Garg is one of the best hernia surgeon in Mohali. He has done many fellowships in minimal access and advanced laparoscopic surgery. He has experience of more than 5000 laparoscopic surgeries, which also include many advanced and complex hernia surgeries. If you are looking for the best hernia surgeon in Mohali, DrAmit Garg is the best
What is a hernia?
A hernia is the term used to define the protrusion of structure or an organ through the muscle that contains it. This is usually seen at places where muscles are weakened due to passage of some structure through the muscles. The most common hernia of abdominal wall is inguinal hernia followed by Para umbilical hernia. Inguinal hernias are 10 times more common in males than females.
What are the common types of hernias?
Inguinal hernias
- In males during development, testes develop inside the abdomen and descend to the scrotum via the lower abdominal wall muscles.
- In males vas deferens passes through the inguinal canal into the scrotum. In some young patients, part of the peritoneum also reaches the testes and through this route the intestine starts protruding into the inguinal canal and this is known as Indirect inguinal hernia.
In patients with history of chronic smoking, cough, heavy weight lifting, chronic straining while micturition or defecation
May cause weakening and rupture of muscles of the posterior layer of Inguinal canal causing protrusion of contents and this type of hernia is known as direct hernia and its common in old age.
Femoral hernias are seen in the upper part of thighs and occur through an opening called Femoral canals. These hernias are rare and seen more commonly in females than males.
Ventral hernias occur through an opening in the muscles
of the anterior abdominal wall.
Keep Reading
Epigastric hernias occur above the bellybutt
Incisional hernias are caused by a weakening of the abdominal muscle resulting from an incision made during a previous abdominal surgery.
Umbilical hernias, which occur near the bellybutton, are most common in newborns, especially those born prematurely. These hernias usually close on their own by the time the child turns 4. Umbilical hernias can be more problematic when they occur in adults.
Hiatal hernias occur when the upper part of the stomach bulges into the chest through a small opening (the hiatus) in the diaphragm. The hiatus allows the esophagus, which carries food from the mouth to the stomach, to pass through the diaphragm.
Dr Amit Garg
Minimal Access Bariatric
Metabolic & GI Surgeon
HERNIA SURGERY
Make An Appointment
Call:6283337650
OR
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some hernia symptoms?
A common symptom of most hernias is a noticeable lump or bulge, and potentially some discomfort or pain. The lump or bulge may not always be present; for example, it might go away when you lie down. Symptoms may worsen when you are standing, straining, or lifting heavy objects. Most hernias can be confirmed by a doctor during a physical exam, but sometimes imaging is necessary.
Hiatal hernia symptoms are an exception to the general rule, as they do not cause a bulge. But hiatal hernias may cause symptoms such as heartburn, acid reflux, and regurgitation of food or liquids, which are often treated with medication.
What are the options for hernia surgery?
Hiatal hernia symptoms can often be treated with medication, but most other types of hernias require surgical repair, although not always immediately. There are two primary options
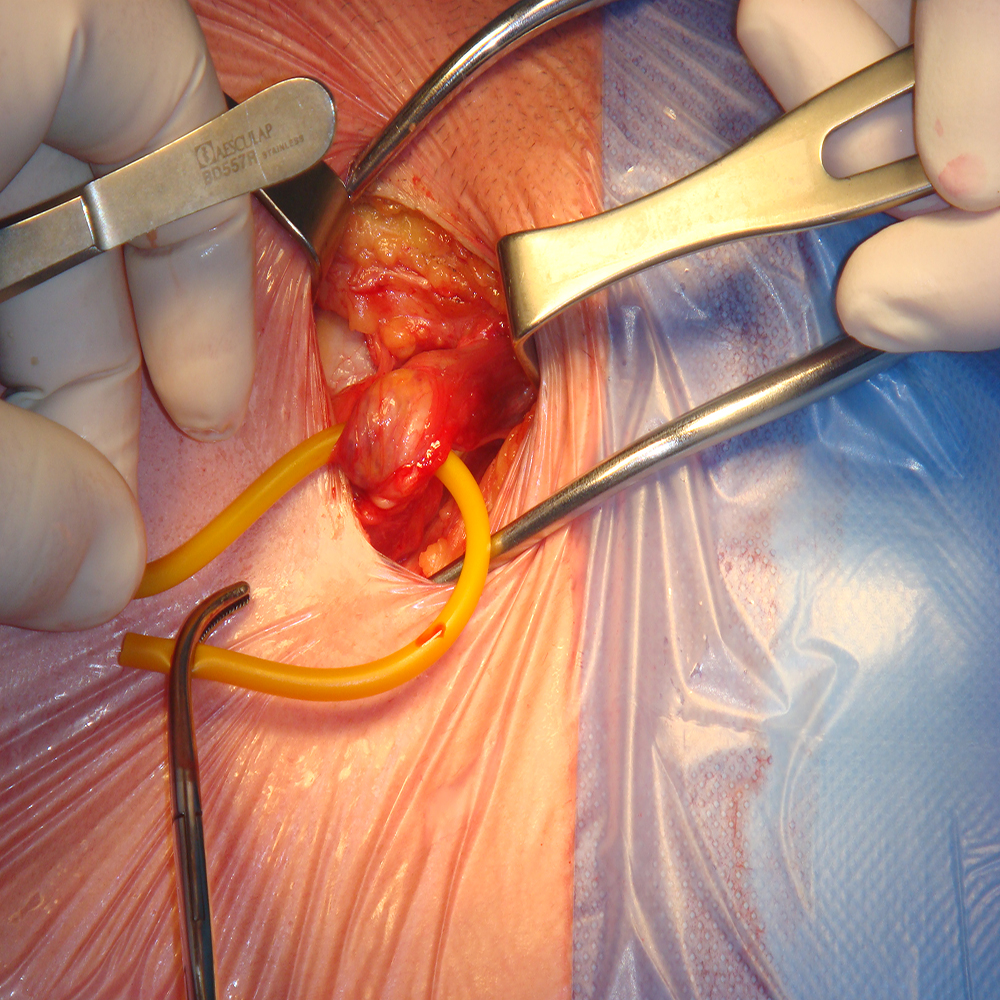
Open hernia surgery. The surgeon makes a cut in the groin to view and repair the hernia. After repairing the hernia, the surgeon uses stitches alone or stitches and a piece of mesh to close the abdominal wall. The mesh is designed to strengthen the weak area of the abdominal wall where the hernia occurred.
Laparoscopic hernia surgery. The surgeon makes several small cuts in the lower abdomen and inserts special tools to view and repair the hernia. The surgeon typically uses a piece of mesh to close and strengthen the abdominal wall. There are some surgeons who opt for robotic repair, which means they sit at a console controlling robotic arms that perform the surgery.
While the use of mesh is predominant and has been shown to help prevent the recurrence of hernias, it also has potential complications, including a risk of chronic pain.
“Despite reduced rates of recurrence, there are situations where the use of surgical mesh for hernia repair may not be recommended,” the FDA advises. “Patients should talk to their surgeons about their specific circumstances and their best options and alternatives for hernia repair.”
What are the alternatives to surgery?
“Watchful waiting” is considered a potential alternative to surgery when a hernia is causing minimal or no symptoms. People who delay surgery, especially men with an inguinal hernia, should watch for symptoms and see a doctor regularly.
About 70% of men with an inguinal hernia who delay surgery will develop new or worsening symptoms and will need surgery within five years, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One risk of waiting too long is that a larger hernia is more difficult to repair.
When might I need emergency surgery?
Seek immediate medical attention if there are signs that your hernia has become stuck or strangulated, which can be life-threatening and usually requires emergency surgery. Signs of this condition include:
A hernia bulge that is suddenly larger than before. A hernia bulge that used to go back inside the abdomen but no longer does
- Fever
- Redness in the area of the hernia
- Sudden or severe pain or tenderness in the area of the hernia
- Symptoms of intestinal obstruction, such as abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting
What type of anesthesia should I receive for surgery?
Several anesthesia options may be discussed with your anesthesiologist, a medical doctor who specializes in anesthesia, pain management, and critical care medicine:
- Local anesthesia with sedation, also referred to as local with monitored anesthesia care, or MAC. This is the most frequently used option. Local anesthesia is usually administered as a one-time injection of medicine that numbs a small area of the body. Sedation relaxes you and is usually administered and adjusted through an IV placed in your arm. The level of sedation can range from minimal (you’ll feel drowsy but able to talk) to deep (you probably won’t remember the procedure).
- Nerve block and sedation. This might be used for inguinal or femoral surgeries, especially if the patient has severe heart or lung disease that precludes the use of general anesthesia. Nerve blocks involve the injection of an anesthetic into specific nerves to block pain signals.
- Spinal block and sedation. This less frequently used option numbs the body from the waist down. The medication for the spinal block is injected through a needle inserted in the lower back into the spinal canal.
- General anesthesia. This type of anesthetic renders you completely unconscious. It also impairs your breathing, so a breathing tube, ventilator, and inhalation anesthetic are used.
Read more...
Discuss the options with the anesthesiologist assigned to your surgery. Anesthesiologists are experts in determining the safest and most effective anesthesia for a particular patient. Although they consider surgeon and patient anesthesia preferences, the type and size of the hernia could preclude some options. For example, general anesthesia is required if the surgeon needs to use a scope during the surgery or if the hernia is particularly large.
The anesthesiologist should ask you about your prior experience with anesthesia and about any anesthesia reactions among your family members, going back multiple generations if possible. You should also be asked about your current health and your health history, including any chronic pain that could make it difficult for you to remain comfortable under sedation instead of general anesthesia.
Let the anesthesiologist know if you use marijuana, CBD products, or other substances, as these can affect the type and amount of anesthesia you can safely receive. You may also be advised to temporarily stop using CBD in the days leading up to and after surgery because of its potential to increase the risk of bleeding.
Less
How can I reduce and manage pain after hernia surgery?
Hernia surgeries typically do not cause a high level of postoperative pain, and most pain can be managed with medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol or other brands) and ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil, etc.). These pain relievers can be supplemented with opioids, although this often is not necessary.
Limiting the use of opioids helps avoid negative side effects, including problems urinating after hernia surgery, which have been known to occur in a minority of patients after inguinal hernia repair. Postoperative urinary retention occurs most often in people over age 50, especially males. Taking medications as directed prior to surgery, including medicines for benign prostatic hyperplasia, which is caused by enlargement of the prostate, also helps prevent postoperative urinary retention.
Under medical direction, measures might also be taken before surgery to limit postoperative pain and nausea, such as taking acetaminophen for pain and a small dose of promethazine to prevent nausea. Consult your anesthesiologist about whether these are appropriate options for you.
How soon can I resume normal activities after hernia surgery?
Your surgeon will provide you with a specific plan but may not be able to give you an exact time frame in advance. Doctors usually cannot fully diagnose the severity of a hernia until they perform the surgery.
Hernia procedures are usually outpatient surgeries. In general, the sooner you can start moving afterward, the better. This movement helps prevent constipation and blood clots. Be sure to adhere to the doctor’s instructions about what you can lift, how to lift, and how long to remain on any restrictions; some may be permanent.
Can hernia surgery result in chronic pain?
Chronic pain affects about 10% of inguinal hernia patients after surgery, according to the International Guidelines for Groin Hernia Management. The guidelines define chronic pain as bothersome moderate pain impacting daily activities for at least three months.
The guidelines also indicate that chronic pain is a higher risk for patients who are young or female, experience high preoperative or high early postoperative pain, have a recurrent hernia, or undergo open repair. Mesh can also cause or contribute to chronic pain. Studies indicate that the risk of chronic pain is less with laparoscopic repair than with open repair, but the type and size of the hernia sometimes preclude the laparoscopic option.
If you suffer from chronic pain, consult with a pain management specialist to consider options such as medication and nerve blocks. Many anesthesiologists are pain management specialists.

Laparoscopic Bariatric & Metabolic Procedures
Bariatric surgery is scientifically proven procedure that aims to help individuals with obesity achieve
significant and sustainable weight loss by altering the digestive system. There are several types of
bariatric procedures, each with its own approach and mechanism of action
Fill our health questionnaire and find out if you are eligible for bariatric surgery
Bariatric Surgery Results



























Bariatric Surgery
Metabolic Surgeries
Laparoscopic GI Surgeries